效果 原生, 没有package.json
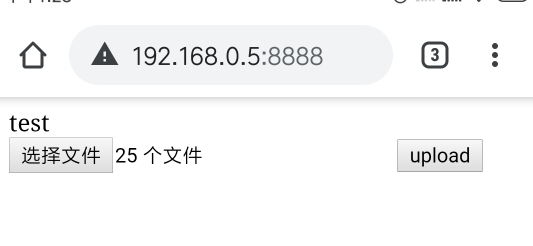
将图片文件上传到电脑上, 项目地址
之后用这个上传了几百张, 超喜欢的图嘿嘿😆
文件上传 平时会碰到上传文件或者用浏览器处理文件等情况, 所以从前后端来写各自的原理与解决方法。
后端的上传处理 - nodejs 原生的 从 nodejs 原生说起
详细可以阅读 http:文件上传背后发生了什么?
服务器接收到文件数据, 下文的 req 便是 http.createSever(function(req, res) {}) 里往匿名回调中传入的参数
1 2 3 4 5 req.on('data' , function (chunk ) console .log(chunk) body += chunk; });
post数据的传输是可能分包的,因此采用监听方式
对数据进行处理
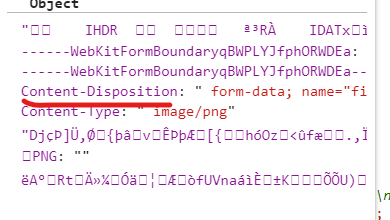
将请求报文转为对象
判断图片文件, 提取信息
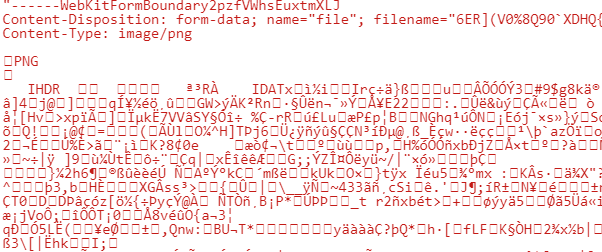
获取文件二进制数据HTTP消息
使用 querystring.parse 获取信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 req.on('end' , function ( var file = querystring.parse(body, '\r\n' , ':' ); if (file['Content-Type' ].indexOf('image' ) !== -1 ) { var fileInfo = file['Content-Disposition' ].split('; ' ); for (value in fileInfo) { if (fileInfo[value].indexOf('filename=' ) != -1 ) { fileName = fileInfo[value].substring(10 , fileInfo[value].length - 1 ); if (fileName.indexOf('\\' ) != -1 ) { fileName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf('\\' ) + 1 ); } } } var entireData = body.toString(), contentType = file['Content-Type' ].substring(1 ); var upperBoundary = entireData.indexOf(contentType) + contentType.length; var shorterData = entireData.substring(upperBoundary); var binaryDataAlmost = shorterData.replace(/^\s\s*/ , '' ).replace(/\s\s*$/ , '' ); var binaryData = binaryDataAlmost.substring( 0 , binaryDataAlmost.indexOf('--' + boundary + '--' ) ); }
http 上传文件, 实际上是由协议 RFC1867 对 form 表单扩展而来的, 如果有兴趣模拟 http 上传文件, 可以看这篇文章, 作者用的是 c# - 模拟HTML表单上传文件(RFC 1867)
将数据写入文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 fs.writeFile('./image/' + fileName, binaryData, 'binary' , function (err ) res.writeHead(200 ); res.end('123' ); });
如果只接收信息不返回的话, 会成为持续连接, 由于浏览器对连接数有最大限制, 所以会出现同时上传文件超过6个很慢的 bug 原文出处 - Max parallel http connections in a browser?
框架的 将来用到再说, 除了原理或者有趣的东西, api 调用什么的是不会调查的, 当然用过的话会写就是了
前端 首先, 上传文件肯定用的是 post , 因为 get 传参放在 url 里有最大值, 而 post 放在 request.body 中没有限制。
首先说明一下 enctype, 用来指示 form 数据形式, 它可以有三种值:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded 正常形式
multipart/form-data 用来传文件
text/plain 不用管
其中 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 是在 headers 部分添加 Entity headers (如果请求中没有 body,则不会包含。), body 是正常 url 编码的值 传达的形式如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 POST / HTTP/1.1 [[ Less interesting headers ... ]] Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Content-Length: 51 text1=text+default&text2=a%CF%89b&file1=a.txt&file2=a.html&file3=binary
而 multipart/form-data 则会在添加 boundary 来区分, 并在最后的 boundary 添加两个连号代表结尾
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 POST / HTTP/1.1 [[ Less interesting headers ... ]] Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=---------------------------735323031399963166993862150 -----------------------------735323031399963166993862150 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="text1" text default -----------------------------735323031399963166993862150 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file1"; filename="a.txt" Content-Type: text/plain Content of a.txt. -----------------------------735323031399963166993862150 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file2"; filename="a.html" Content-Type: text/html <!DOCTYPE html><title>Content of a.html.</title> -----------------------------735323031399963166993862150--
详细可以看这里 What does enctype=’multipart/form-data’ mean?
历史演变 submit form -> XMLHttpRequest form
form 提交会默认跳转新页面, 默认使用 GET, 如果用 POST, 那么请求报文中的 content-type 默认为 x-www-form-urlencoded
提交需要使用设置了 type=”submit” <input> 或 <button> 当然 js 也可以
详细提交方式可以看 - form表单提交方式
另外插件 jquery.form.js 不跳转上传, 原理为: ajax + 取消默认事件如果不支持 XMLHttpRequest 2级使用 target + iframe
由于懒, 不想用 postman 之类的, 直接用 node 来看请求报文, 使用 nodejs 监听源自本机上所有的访问次端口的请求, 并打印请求中的信息, 原文来自 - HTTP test server accepting GET/POST requests
ajax 上传 到了 ajax 的时候, 可以用 FormData 对象管理表单数据, FormData 类型其实是在 XMLHttpRequest 2级定义的, 可以利用 HTMLFormElement 对象初始化来获得与表单相同的值, 相比一个个获取表单值再上传方便
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var req = new XMLHttpRequest();req.open('post' , '/uploadUrl' ); var test = new FormData()test.append("k1" , "v1" ); req.send(test); req.open('post' , '/uploadUrl' ); req.send(123 )
FormData 会自动在上传的时候设置 content-type, 原文来自 - axios的content-type是自动设置的吗?
应用 最后来写下我的应用:
场景: 手机上有很多好看的图片, 但是我平时欣赏图片一般是电脑上, 所以想把图片传上来
应该够清楚了吧, 接下来贴代码啦
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 var http = require ('http' );var fs = require ('fs' );var querystring = require ('querystring' );const portal = 8888 ;console .log(`服务开始,打开localhost:${portal} 即可访问` );http .createServer(function (req, res ) var arg = req.url; if (arg === '/uploadUrl' ) { console .log('上传文件服务' ); parseFile(req, res); } else { fs.readFile('./test.html' , 'utf-8' , function (err, data ) if (err) throw err; res.writeHead(200 , { 'Content-Type' : 'text/html' }); res.write(data); res.end(); }); } }) .listen(portal); function parseFile (req, res ) req.setEncoding('binary' ); var body = '' ; var fileName = '' ; var boundary = req.headers['content-type' ].split('; ' )[1 ].replace('boundary=' , '' ); req.on('data' , function (chunk ) console .log(typeof chunk); body += chunk; }); req.on('end' , function ( var file = querystring.parse(body, '\r\n' , ':' ); if (file['Content-Type' ].indexOf('image' ) !== -1 ) { var fileInfo = file['Content-Disposition' ].split('; ' ); for (value in fileInfo) { if (fileInfo[value].indexOf('filename=' ) != -1 ) { fileName = fileInfo[value].substring(10 , fileInfo[value].length - 1 ); if (fileName.indexOf('\\' ) != -1 ) { fileName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf('\\' ) + 1 ); } } } var entireData = body.toString(), contentType = file['Content-Type' ].substring(1 ); var upperBoundary = entireData.indexOf(contentType) + contentType.length; var shorterData = entireData.substring(upperBoundary); var binaryDataAlmost = shorterData.replace(/^\s\s*/ , '' ).replace(/\s\s*$/ , '' ); var binaryData = binaryDataAlmost.substring( 0 , binaryDataAlmost.indexOf('--' + boundary + '--' ) ); fs.writeFile('./image/' + fileName, binaryData, 'binary' , function (err ) res.writeHead(200 ); res.end('123' ); }); } else { res.end('just pic allowed' ); } }); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 <form id ="form" action ="/uploadUrl" enctype ="multipart/form-data" method ="post" > <input type ="file" name ="upload" multiple /> <input type ="button" value ="upload" onclick ="handler(this)" /> </form > <script > var files; function handler (e ) var trueForm = document .getElementById('form' ); var form = new FormData(trueForm); files = form.getAll('upload' ); iterate(0); } function iterate (num ) Promise .all( files.slice(num, num + 6).map( (i) => new Promise ((res, rej ) => { upload(i, res); }) ) ) .then((result ) => { if (num >= files.length - 6 ) return ; iterate(num + 6); }) .catch((result ) => { if (num >= files.length - 6 ) return ; iterate(num + 6); }); } function upload (i, res ) var temForm = new FormData(); temForm.append('file' , i); var req = new XMLHttpRequest(); req.onreadystatechange = function ( if (req.status == 200 ) { res(); } }; req.open('post' , '/uploadUrl' ); req.send(temForm); } </script >
参考文章 :